Some pandas tricks 1
Теги:
Import an [sqlalchemy] table to a [pandas] dataframe
table_df = pd.read_sql(
'SELECT * from game',
session_remote.bind
)
How to calculate summary statistics
Aggregating statistics

titanic["Age"].mean()
Out[4]: 29.69911764705882

titanic[["Age", "Fare"]].median()
Out[5]:
Age 28.0000
Fare 14.4542
dtype: float64
titanic[["Age", "Fare"]].describe()
Out[6]:
Age Fare
count 714.000000 891.000000
mean 29.699118 32.204208
std 14.526497 49.693429
min 0.420000 0.000000
25% 20.125000 7.910400
50% 28.000000 14.454200
75% 38.000000 31.000000
max 80.000000 512.329200
# or
titanic.agg(
{
"Age": ["min", "max", "median", "skew"],
"Fare": ["min", "max", "median", "mean"],
}
)
Out[7]:
Age Fare
min 0.420000 0.000000
max 80.000000 512.329200
median 28.000000 14.454200
skew 0.389108 NaN
mean NaN 32.204208
Aggregating statistics grouped by category
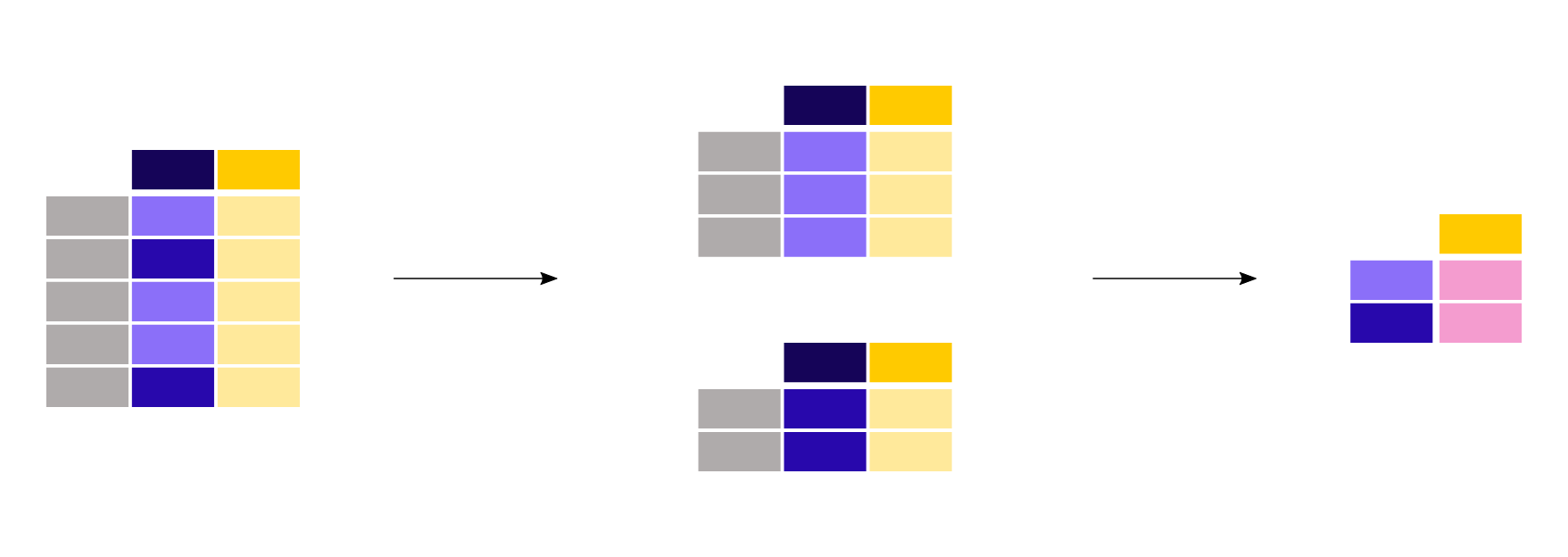
titanic[["Sex", "Age"]].groupby("Sex").mean()
Out[8]:
Age
Sex
female 27.915709
male 30.726645
Count number of records by category
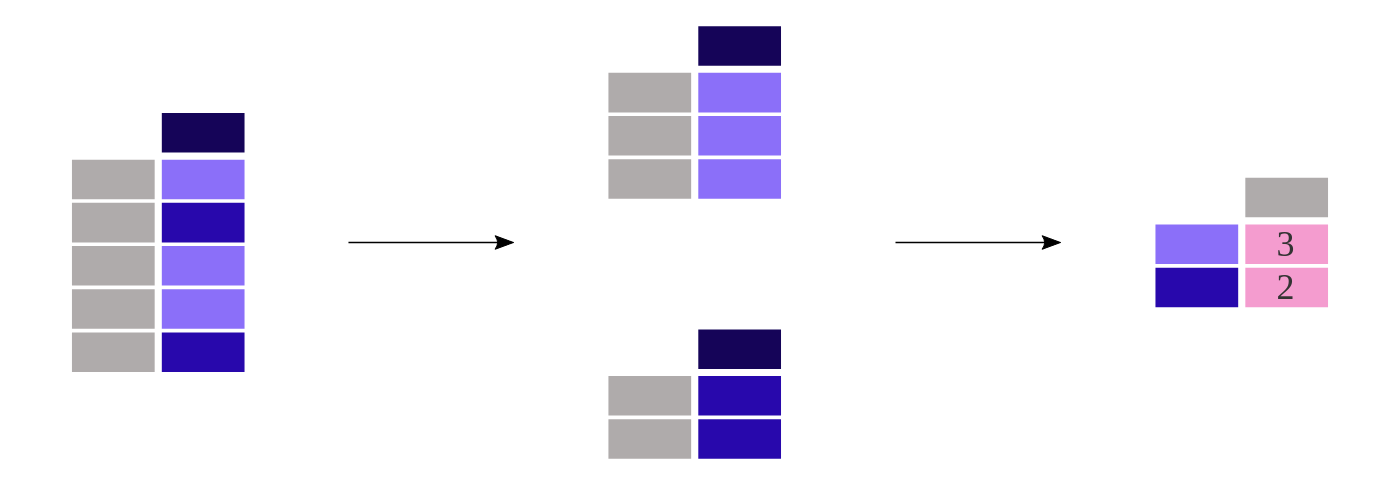
titanic["Pclass"].value_counts()
Out[12]:
3 491
1 216
2 184
Name: Pclass, dtype: int64
# or
titanic.groupby("Pclass")["Pclass"].count()
Out[13]:
Pclass
1 216
2 184
3 491
Name: Pclass, dtype: int64
How to calculate summary statistics
How do I select rows from a DataFrame based on column values
df.loc[df['column_name'] == some_value]
df.loc[df['column_name'].isin(some_values)]
df.loc[(df['column_name'] >= A) & (df['column_name'] <= B)]
# Note the parentheses. Due to Python's operator precedence rules, & binds more tightly than <= and >=. Thus, the parentheses in the last example are necessary. Without the parentheses
df.loc[df['column_name'] != some_value]
df.loc[~df['column_name'].isin(some_values)]
How to select rows with one or more nulls from a pandas DataFrame without listing columns explicitly
In [60]: df[pd.isnull(df).any(axis=1)]
Out[60]:
0 1 2
1 0 NaN 0
2 0 0 NaN
Set value of one column based on value in another column
df.loc[df['c1'] == 'Value', 'c2'] = 10
Replacing Rows in Pandas DataFrame with Other DataFrame Based on Index
df1.update(df2)
>>> df1
B C
A
0 300.0 6.0
1 400.0 7.0
2 433.0 99.0
3 555.0 99.0
Or use df1.combine_first(df2). Source
Deleting DataFrame row in Pandas based on column value
df = df[df.line_race != 0]
Use [tqdm] Progress Bar with Pandas
for index, row in tqdm(df.iterrows(), total=df.shape[0]):
print("index",index)
print("row",row)
Most straightforward row iteration with [pandas]
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
for index, row in df.iterrows():
print(row, '\n')
# or itertuples()
species_labels = {'setosa': 0, 'versicolor': 1, 'virginica': 2}
for row in df.itertuples():
label = species_labels[row.species]
df['species'].at[row.Index] = label # update the row in the dataframe
# or apply()
species_labels = {'setosa': 0, 'versicolor': 1, 'virginica': 2}
df['species'] = df.apply(lambda row: species_labels[row['species']], axis=1)
# or map()
species_labels = {'setosa': 0, 'versicolor': 1, 'virginica': 2}
df['species'] = df['species'].map(species_labels)
How to show PIL Image in ipython notebook
from IPython.display import Image
pil_img = Image(filename='data/empire.jpg')
display(pil_img)
# or
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
%matplotlib inline
pil_im = Image.open('data/empire.jpg', 'r')
imshow(np.asarray(pil_im))
# or
from PIL import Image # to load images
from IPython.display import display # to display images
pil_im = Image.open('path/to/image.jpg')
display(pil_im)
IPython Notebook output cell is truncating contents of my list
pd.options.display.max_rows = 4000
This can be used as context. Source
Смотри еще:
- Pandas Getting started tutorials
- [pandas]
- [2022-07-23-daily-note] Some tricks for creation, get values, set new columns and groupby
- [lists/sqlalchemy]
- [tqdm]
- [PIL]